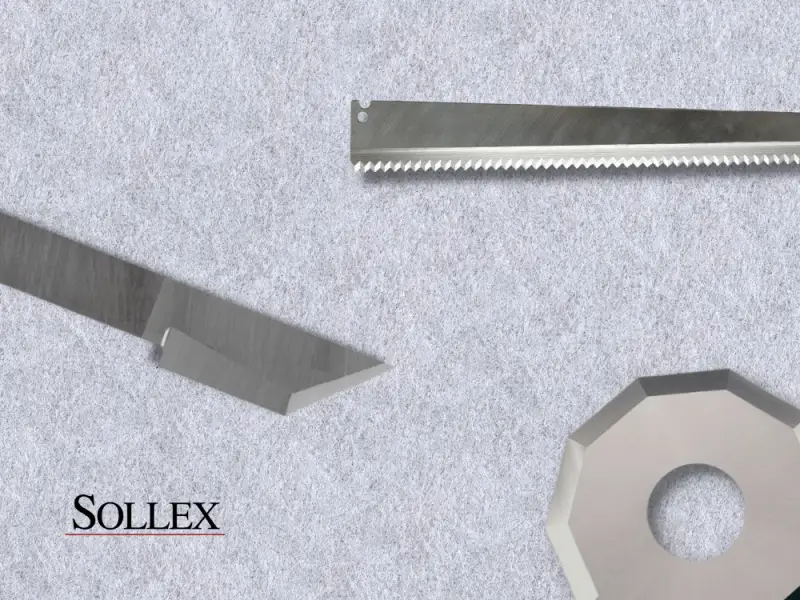
Industrial Cutting Methods for Nonwoven Fabrics
About types of nonwovens, production methods and cutting techniques
Non-woven fabric has a wide range of applications and many advantages and limitations. In this article we discuss this material with a focus on how nonwovens are produced and cut in industrial production.
Content:
- Non-woven Material and Applications
- Nonwovens Manufacturing Techniques
- Recycling of Nonwoven
- Common Industrial Cutting Methods for Non-woven
- Buy Machine Blades for Cutting of Nonwoven Fabrics
Non-woven Material and its Applications
Nonwoven fabrics are a type of textile material made from fibers that are not woven, like textiles, and not glued together, but interwoven. Synthetic fibers, natural fibers or a mixture of both can be used in nonwovens. Depending on the end-use application, nonwovens can be made from a variety of materials.
| Material | Description |
|---|---|
| Synthetic polymers | These are the most common materials used to make nonwovens. Examples include polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), polyethylene (PE) and nylon. |
| Natural fibers | Nonwovens can be made from natural fibers such as cotton, wool and viscose. |
Recycled materials | Nonwovens can also be made from recycled materials, such as recycled PET bottles, which can be melted down and spun into fibers. |
| Blends | Nonwovens can be made by blending different types of fibers, such as a blend of synthetic and natural fibers, to achieve specific properties. |
The fibers are usually held together by heat, chemicals or mechanical processes such as needle punching or hydro weaving.
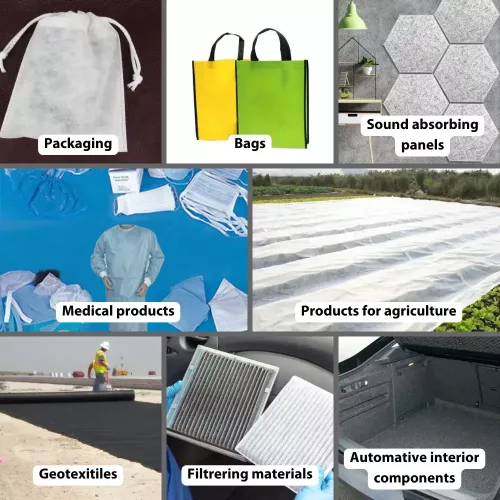

Nonwovens are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Packaging materials such as shopping bags, gift wrap, etc
- Medical products such as surgical gowns, masks and curtains
- Personal care products such as nappies and sanitary towels
- Filtering materials
- Geotextiles for construction and agriculture
- Automotive interior components
Nonwovens have a number of advantages over traditional woven materials, including lower cost, greater flexibility and the ability to produce materials of varying thickness and density. They also have good strength, durability and absorbency.
Although nonwovens have many advantages, they also have some disadvantages: lower strength than fabrics and limited recyclability. Nonwovens are difficult to recycle and some nonwovens may require the use of chemicals that can have an impact on the environment.
Nonwovens Manufacturing Techniques

Non-woven fabric production method | Description |
|---|---|
Spunlacing | Spunlace nonwovens are made by using high-pressure water jets to entangle fibers to form a fabric. Examples include rayon spunlace nonwovens, which are used as wipes and in medical applications. |
Needlepunching | Needle-punched nonwovens are made by piercing the fibers with needles, which weave together to form a uniform nonwoven fabric. For example, needle-punched polyester nonwovens are used for insulation and geotextiles. This process can be repeated several times to produce fabrics of varying thickness and density. |
Wet laying | Wet laying nonwovens are made by slurrying the fibers in water and then forming a web by draining the water and bonding the fibers together using heat or chemicals. As an example, cellulose-based nonwovens are used as tissues and for medical purposes. |
Spunbonding | Spunbond nonwovens are made by extruding melted polymer through spinnerets to form continuous filaments that are laid down in a random pattern to form a web. Heat or chemical adhesives are used to bond the filaments together to form a nonwoven fabric. Examples include polypropylene (PP) spunbond nonwovens. |
Melt Blowing | Melt blowing is a process similar to spunbonding, but it produces finer fibers and is often used to produce materials with a higher degree of filtration efficiency. Meltblown nonwovens are made by extruding melted polymer through small nozzles to form microfibers that are laid down in a random pattern to form a web. Examples include PP meltblown nonwovens, which are commonly used in face masks and filters. |
Consequently, we distinguish the following main types of nonwoven materials: Spunbond Nonwoven Fabrics, Needlepunch Non-Woven Fabric, Wet-laid Nonwoven Fabrics, Spunlace Nonwoven Fabrics, Melt-blown Nonwoven Fabrics.
Recycling of Nonwoven
A common recycling method for nonwovens is mechanical recycling, which involves shredding the fabric into small pieces and then using those pieces to create new nonwovens or other products. This method is particularly suitable for nonwovens made from thermoplastic polymers such as polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET), which can be melted and spun into new fibers.
How Manufacturers Cut Nonwoven Materials
After the material has been produced, it must be cut into desired widths and, for example, wound onto reels if it is a thin nonwoven material, or into plates if the nonwoven material is thicker. The final product is produced in a subsequent production stage, where cutting may also be necessary.
Industrial cutting method for non-woven fabric | Description |
|---|---|
Rotary cutting | Industrial rotary cutting machines are usually automated and can cut thick or several layers of nonwovens at the same time. In this process, the material is fed through a machine that uses a rotating circular knife to cut the material into the desired width. The trick for cutting nonwoven with rotary cutting is to have an extra long and sharp grinding on the circular blade. We manufacture and re-sharpen circular knives for cutting various nonwoven materials. If you have any questions, email us at info@sollex.se |
Razor slitting | Cutting thin nonwovens wrapped on spools is also possible with industrial blades. In this case this is done on a rewinder machine and the material must also be tensioned so that the blade can easily cut through the material. Usually the blade has additional coatings on the cutting edges to improve performance and reduce heat build-up on the blade when cutting. Sollex blades 5K, 5Z as well as 2-013-Z showed excellent results when cutting thin nonwovens |
Plotter cutting | Nonwoven material can be cut by a plotter (cutter / digital cutting system) using a process of CNC cutting. The nonwoven material is placed on the cutter table, where a vacuum holds the material firmly while cutting. An oscillating knife then cuts the material, most often of complex designs and patterns. Digital cutting with a plotter offers a high degree of precision and accuracy, making it well-suited for cutting complex shapes and patterns in nonwoven materials. |
Die-cutting | Punching is a process in which a die is used to give nonwovens a specific shape. Dies are special tools made of metal or other materials that are given the desired shape or pattern. The material is placed between the die and a cutting press. Pressure is applied to give the material the required shape. Die-cutting can also include cutting with straight serrated / toothed knives, which technically perform a similar action - a sharp vertical movement cuts the material, cutting off the desired length. Sollex makes these toothed knives to order. All machine knives are not listed on the website, but you can write to us and ask. |
Ultrasonic cutting | An ultrasonic cutting machine cuts non-woven materials by applying ultrasonic vibrations to a cutting knife. It is a fast and accurate cutting method that can be used to cut complex shapes and patterns. The ultrasonic knife cutting technique is similar to cutting with an oscillating knife, only the speed of the knife is hundreds of times faster. |
Laser cutting | Laser cutting involves the use of a high-powered laser to cut through nonwoven materials. In the manufacture of medical and hygiene products such as surgical masks and gowns, laser cutting is commonly used. |
For cutting, the thickness of the nonwoven material can affect the type of cutting method used, as well as the cutting parameters such as blade depth and speed. Thicker nonwoven materials may require more force or a different type of cutting tool, such as a rotary blade, to achieve a clean and accurate cut.
All of these methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on specific application requirements, such as desired accuracy, cutting speed, and nonwoven material properties. Manufacturers can also use a combination of cutting methods to achieve the desired end product results.
Buy Machine Blades for Cutting of Nonwoven Fabrics
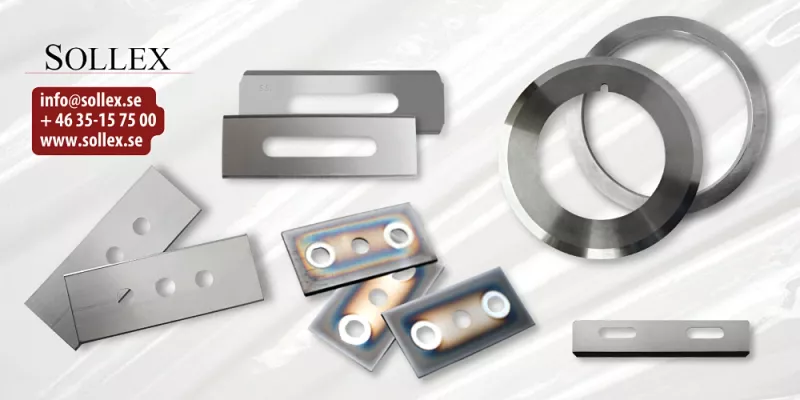
As we mentioned above, Sollex produces knives for cutting nonwovens such as: circular knives, toothed knives, oscillating knives for cutting on digital plotter cutting systems, long straight blades and even adapted blades for ultrasonic cutting. If you have a drawing - great, send us an email at info@sollex.se and we'll send you an offer with the best price and delivery time.

___
Sollex is a Swedish supplier of industrial knives and machine blades! We have cutting products with cutting-edge technology and performance that improve manufacturing and converting processes and solve problems. With the right knives and blades you can get simplified maintenance, time savings and an improved end product.
You are welcome to contact us with your questions:
Company name: Sollex AB
Customer service and orders: order@sollex.se
Telephone: +4635–15 75 00
Address: Box 5161, 200 71, Malmö, Sweden