Plastic Film Slitter Rewinder Machines & Slitter Blades: Overview
In this article we will look at slitting and rewinding machines that are used for cutting and converting plastic film, as well as understand their features, and reveal which slitter knives are the best for slitting different types of film.
Content:
- About Slitter Rewinders
- Plastic Film Cutting
- Use of SR Machines
- Types of SR Machines
- Knives & Blades for SR
- Choice of the Right Slitter Knife
- Tips on How to Choose Slitter Blades
Slitter Rewinder Machines: Definition
Slitter rewinders are industrial machines used by plastic film manufacturers to slit in-line plastic film, trim its rough edges and then wind it onto reels and spools, as well as by specialized companies that convert and fit film for other companies by laminating, perforating and lately cutting it into smaller rolls.

There are a large number of slitter rewinder machine manufacturers in the world and here are some of them: KAMPF Machinery Corp., Atlas Converting Equipment Ltd, ASHE Converting Equipment, ALPINE, GOEBEL IMS, Bandera, Bimec, Cattorini, Catbridge, Cerutti, Dolci, JURMET, ELTEX, Polyrema Reifenhäuser, Primplast, SCAL, Sitec, TITAN ComMachinery, UTECO.
Manufacturer | Types of Slitter Rewinder Machines |
|---|---|
Accraply (Stanford) | Flexible packaging systems, high-speed slitter rewinders |
Converting Equipment Intl (CEI) | Label slitter rewinders, high-speed, ergonomic designs |
Ribamatic | Roll slitting and rewinding machines for various industries |
Jennerjahn Machine | Cored surface slitter rewinders, coreless surface slitter rewinders, center slitter rewinders |
Catbridge Machinery | Duplex center/surface slitter rewinders, two-drum surface winders |
Deacro Industries | Cantilevered slitter rewinders, turret slitter rewinders |
Parkinson Technologies (Dusenbery) | Center slitter rewinders, center surface slitter rewinders, surface slitter rewinders, single knife cutters |
Elite Cameron | Center winders, center surface winders, turret winders, two-drum surface winders |
Ashe Converting Equipment | Versatile slitter rewinders for converting industry |
Atlas Converting Equipment | Titan series slitter rewinders for various materials |
Kampf Schneid- und Wickeltechnik | High-performance slitter rewinders for film, foil, and flexible materials |
Goebel IMS | Precision slitter rewinders for paper, board, and nonwovens |
Euromac | Heavy-duty slitter rewinders for various applications |
Universal Converting Equipment | Customizable slitter rewinders for diverse materials |
Laem System | Innovative slitter rewinders with automation features |
Erhardt+Leimer | Automated slitting and winding technology |
Nishimura Mfg. Co., Ltd. | Specialized slitter rewinders for packaging and converting |
Rotoflex | Inspection, slitting, and rewinding machines for label and packaging industries |
Kendall Packaging Corporation | Slitter rewinders for flexible packaging materials |
Elite Cameron (emphasis) | Reliable and high-quality slitter rewinders for diverse applications |

Roll slitter rewinder machines are used to cut a huge variety of different flexible materials such as paper, adhesive tape, labels, metallized or aluminum foil, ribbons, textile, so they vary in their specifications and design. However, slitter machines are most often used for slitting different types of plastic films.
Plastic Film for Slitter Cutting
Slitter rewinders play a vital role in the production, converting and processing of plastic films for food packaging, non-food packaging films, sacks and bags, agricultural films, building and construction films. Plastic film slitter rewinders are designed to handle various types of plastic films, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and others. Each type of film may have different properties such as thickness, flexibility, and surface characteristics, which the machine needs to accommodate.
Plastic film slitter rewinders are capable of handling various types of plastic films, including:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyester (PET)
- Linear Low-density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
- Low-density Polythene (LDPE)
- Bi-axially-orientated Polypropylene Polymer (BOPP)
- Bi-axially-oriented Polyethylene (BOPE)
- Biaxially-oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate (BOPET)
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PETE)
- Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)
- Laminates etc
Therefore there is a wide array of slitting machines for different types of plastic film, such as: PVC or vinyl film slitter rewinder, shrink film slitting rewinding machine, stretch film slitting rewinding machine, polyester film slitting rewinding machine, LLDPE stretch film slitting rewinding machine, BOPP film slitting rewinding machine, PET film slitting rewinding machine, laminated film slitter rewinder machine and so on.
Use of Slitter Rewinder Machines
Slitter rewinders are versatile machines utilized by both film manufacturers and companies engaged in the conversion of flexible packaging. Let's examine how each of these industries utilizes slitter rewinders.
Film Manufacturers
Film manufacturers, such as Amcor plc, Berry Global, Trioworld, Winpack, are primarily responsible for the production of large rolls of plastic film, foil, or other flexible substrates in a variety of plastic polymers, widths, and thicknesses. Slitters are typically used in-line to trim edges and slit these large master rolls into narrower rolls of specified widths in the film manufacturing process. Once the rolls have been slit, they are typically rewound onto smaller cores. Prior to distribution to customers or film converters, the rolls may undergo additional processes such as inspection, packaging, and labeling. Most commonly, such reeled film is further customized and converted into products.

Film manufacturers are focused on efficiently producing high quality film rolls and can utilize the services of converting companies to add value to their products and meet the diverse needs of end users in various industries.
Film & Flexible Packaging Converting Companies
Flexible packaging companies purchase rolls of film from film manufacturers. These companies then process the rolls to create finished packaging products that meet specific customer requirements. This additional processing may include printing, laminating, perforating, cutting to a specified width, pouch making, and other processes designed to add value and customize packaging for specific products or brands.

Types of Slitter Rewinder Machines
There are several other types of slitter rewinders, each designed to meet specific requirements and applications. There are 3 main winding techniques: center winding, surface-center winding and surface winding, where center-winding is the most common technique. Duplex winder machine is the most common type of center winding.
Type name |
Specification |
|---|---|
Duplex Slitter Rewinder Machine |
A duplex slitter rewinder machine features two rewind shafts or stations, allowing simultaneous processing of two rolls of material. This configuration enhances productivity by enabling continuous operation and reducing downtime for roll changes. |
Duplex Center Slitter Rewinder Machine | A duplex center slitter rewinder machine combines the features of duplex and center slitter rewinders, offering two rewind shafts positioned at the center of the machine. This configuration enables simultaneous processing of two rolls with precise tension control, suitable for medium to high-volume production. |
Duplex Surface Center Slitter Rewinder | A duplex surface center slitter rewinder features dual unwind and rewind stations for simultaneous processing, ensuring high productivity. Its precision center slitting mechanism guarantees uniform cuts, while the surface winding system maintains consistent tension for impeccable rewound rolls. |
Duplex Differential Shaft Slitter Rewinder | This type of slitter rewinder features differential shafts for rewinding, allowing for precise tension control and accommodating a wide range of core sizes. It is suitable for processing flexible materials such as films, foils, and laminates. |
Duplex Differential Rewind Slitter Rewinder | This type of slitter rewinder combines the differential shafts of the Duplex Differential Shaft Slitter Rewinder with the dual-rewind capability of the Duplex Center Surface Slitter Rewinder. It offers precise tension control and high productivity, making it suitable for a wide range of materials and applications. |
Single Shaft Slitter Rewinder | In this configuration, a single shaft is used for rewinding the material. It is suitable for processing narrower rolls and is often used in smaller-scale operations or for specialty applications. |
Turret Slitter Rewinder | Turret rewinders feature multiple rewind shafts mounted on a rotating turret. This design allows for quick and efficient roll changes, minimizing downtime between production runs. Turret slitter rewinders are commonly used in high-speed, continuous production environments. |
Center Winder Slitter Rewinder | In this type of machine, the material is rewound onto a single large-diameter core mounted on a center winder. Center winder slitter rewinders are suitable for processing wide web materials and are often used in industries such as paper manufacturing and converting. |
Surface Rewind Slitter Rewinder | Surface rewinders rewind the material with the surface facing outward. They are commonly used for applications where roll diameter consistency is crucial, such as in printing and laminating processes. |
Narrow Web Slitter Rewinder | The narrow web slitter rewinder is a compact and space-efficient machine designed specifically for handling narrow-width materials. Despite its smaller size, it offers precision slitting capabilities to ensure accurate cutting of materials such as films, tapes, and labels. |
The capacity of a slitter rewinder machine can vary widely depending on several factors. Some slitter rewinders have multiple slitting stations, allowing them to simultaneously slit multiple rolls of material. Machines with more slitting stations generally have higher capacity. Different roll materials have different properties, such as thickness, width, and tensile strength, which can affect the machine's capacity. For example, a slitter rewinder may have a higher capacity for thin plastic films compared to thick metal foils.
Knives and Blades for Slitter Rewinders
The cutting technique in plastic film slitting and rewinding machines is usually longitudinal, hence the use of rotary knives or industrial razor blades. Slitter machines use different types of rotary and razor blades depending on the material being cut, and here are some common types of blades used in slitting machines.
Industrial Razor Blades for Film Slitting
These are the most straightforward type of knives used in slitter rewinders. They are essentially fixed blades that the material is pulled over. Razor blades are especially effective for very thin materials, offering a clean cut due to their sharpness. However, they tend to dull quickly and need frequent replacement. They are best suited for applications where precision is critical and the material is not too thick. Razor blades are sharp, thin blades commonly used for slitting thin materials such as paper, plastic films, and foils. They provide clean and precise cuts and are suitable for high-speed slitting operations. Read more about razor slitting here.

Circular Knives for Plastic Film Slitting
Circular knives, also known as rotary knives or disc knives, are circular-shaped blades mounted on a rotating shaft. They are versatile and can be used for slitting a wide range of materials, including paper, films, textiles, and non-woven materials.
Shear Blades for Plastic Film Slitting
Shear cut blades, also known as top and bottom circular knives, consist of two opposing blades that move in a scissoring motion to cut the material. They are typically used for slitting thick or rigid materials that require extra cutting force, such as laminates, multilayers, foils. Shear slitting is preferred for materials that require a cleaner edge and can include everything from thin films to thicker papers and laminates. The shear blades can be adjusted for different materials, making them highly versatile. Read more about shear cutting here.
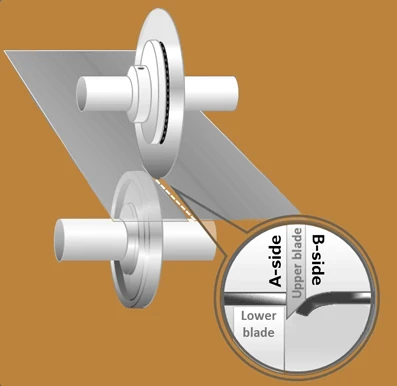
Crush Cut Blades for Plastic Film Slitting
Crush cut blades consist of a circular blade mounted against an anvil roll. They operate by crushing and cutting the material against the anvil roll, making them suitable for slitting delicate or stretchy materials that may deform under pressure. This method is often used for materials where the precision of the cut edge is not as critical, such as some types of tape, paper and board. The score slitting technique is robust and can handle materials that are difficult to cut with other methods. However, the crushing action can sometimes deform the edges of the material being slit. Read more about crush cutting here.

The selection of the appropriate type of knife depends on factors such as the material's thickness, elasticity, surface characteristics, and desired slit quality.
Here's a summary table of the different types of knives used in slitter rewinders, including their usage, advantages, and disadvantages:
| Knife Type | Usage | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Razor Blades | Thin materials like films, foils, paper | Simple design, cost-effective, easy to replace, fine cuts | Wears out quickly, limited to thinner materials |
| Shear Blades | Wide range of materials (films, foils, laminates, paper, nonwovens) | Clean and precise cuts, durable, versatile | Complex setup and maintenance, more expensive |
| Score (Crush) Knives | Materials like paper, board, laminates | Simple design, good for bulkier materials, cuts multiple layers | May deform material, less precise than shear blades |
Razor blades are best for thin and delicate materials, shear blades offer versatility for different thicknesses, and score knives are suited for tougher, bulkier materials. For applications requiring clean edges, shear blades are preferred. For less critical edge quality, score knives are suitable. Razor blades are inexpensive and easy to replace but require frequent changes. Shear blades are more costly but provide longer-lasting, higher-quality cuts. Score knives balance cost and durability but are less precise.
By choosing the appropriate knife type, manufacturers can optimize the slitting process for different materials and applications, ensuring efficient and high-quality production.
The Best Slitter Blades for Plastic Film Converting
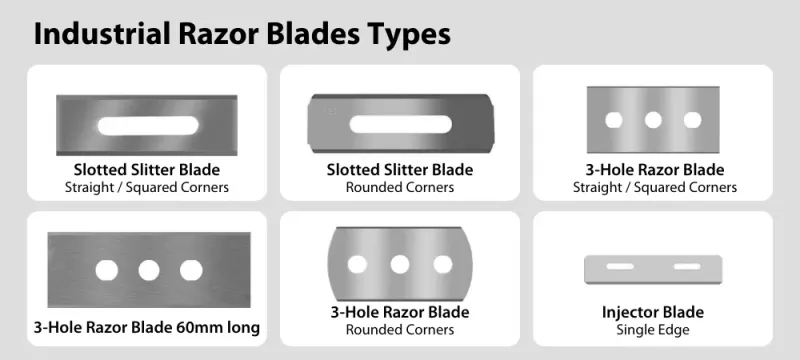
The choice of knife largely depends on the thickness and type of material being processed. Razor blades are best for thin and delicate materials, while shear blades offer versatility for a range of thicknesses, and score knives are suited for tougher, more robust materials.
Razor blades are known for their exceptionally sharp edges, which allow for clean and precise cuts through various materials, including paper, plastic films, foils, and laminates, but industrial razor blades are mainly used and even recommended for slitting of plastic film, stretch film and light aluminum foils. With industrial razor blades you will get the best possible cut when cutting plastic film.
 Razor blades are widely used in slitting machines and similar converting equipment due to their sharpness, accuracy, ease of installation and versatility in cutting a wide range of materials. Razor blades typically have a thin kerf, or cutting width, which minimizes material waste and allows for narrow slit widths, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision and tight tolerances.
Razor blades are widely used in slitting machines and similar converting equipment due to their sharpness, accuracy, ease of installation and versatility in cutting a wide range of materials. Razor blades typically have a thin kerf, or cutting width, which minimizes material waste and allows for narrow slit widths, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision and tight tolerances.
Razor blades mounted at an angle in special blade holders or in cassettes of several pieces are used to cut the moving web material. Slitter blades have a variety of designs that do not really play a major role in their cutting functionality, but the blade thickness, the material they are made of, and the additional coating play a role. So when choosing an industrial blade for cutting film or other materials pay attention to the above factors.
There are two-hole, three-hole, and longitudinal slotted blades, the choice of which depends on the blade holder design. Also blades can have both rounded and straight corners. It is noteworthy that the blades are rectangular and consequently have 4 cutting sides, which is very economical, as the blades can be turned over and reused.
Typical problems with razor cutting are: edge quality problems for thicker and denser materials in the form of a raised edge, possible disruption of the multilayer film surface coating, filament, dust, and " angle hairs" along the slit edge. It should also be noted that too thin industrial blades can vibrate at high speeds and thus making the cutl deteriorate. Also with additional coating on the edges, if the films contain too many additives and can be said to be abrasive in composition, ceramic slitter blades are the only option.
3-Hole Razor Blades for Plastic Film Slitter
Industrial 3-hole blades are one of the most popular choices for cutting plastic film in slitters. Below is a selection of straight edge blades from Sollex. You can find blades with rounded edges here. All blades are packed in industrial grade packaging and are vacuumed.
SKU | Product | Application | Thick., mm | Pack,pcs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Stainless steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.10 | 250 | |
Stainless steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.13 | 250 | |
No oil | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.13 | 250 | |
Ceramic | White plastic film with additives | 0.13 | 250 | |
Titanium | Plastic film and foil with few additives | 0.13 | 250 | |
Zero Friction | Thin stretched film | 0.13 | 250 | |
Full Ceramic | Plastic film with additives, multilayer | 0.13 | 30 | |
Solid Ceramic | Soft flexible film folies (EBA) | 0.13 | 10 | |
Titanium | Plastic film and foil with few additives | 0.15 | 200 | |
Stainless steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.20 | 200 | |
Ceramic | White plastic film with additives | 0.20 | 200 | |
Titanium | Plastic film and foil with few additives | 0.20 | 200 | |
Zero Friction | Thin stretched film | 0.20 | 200 | |
Full Ceramic | Plastic film with additives, multilayer | 0.20 | 10 | |
Solid tungsten carbide | Hard laminated films (PE) and packaging | 0.20 | 10 | |
Titanium | Plastic film and foil with few additives | 0.23 | 100 | |
Carbon steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.30 | 100 | |
Stainless steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.30 | 100 | |
Ceramic | White plastic film with additives | 0.30 | 100 | |
Full Ceramic | Plastic film with additives, multilayer | 0.30 | 30 | |
Solid tungsten carbide | Hard laminated films (PE) and packaging | 0.30 | 10 | |
Carbon steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.40 | 100 | |
Carbon steel | Simple plastic films with few additives | 0.68 | 50 |
Slotted Slitter Blades for Film Slitter Rewinders
Slotted slitter blades come with straight or rounded corners. Thickness of such slitter blades are 0.20, 0.38 and 0.40mm.
SKU | Product | Application | Thick., mm | Pack,pcs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Carbon steel | Simple plastic with few additives | 0.20 | 200 | |
Ceramic | White plastic film with additives | 0.40 | 100 | |
Stainless steel | Simple plastic with few additives | 0.40 | 100 | |
Solid tungsten carbide | Hard laminated films (PE) and plastic packaging | 0.38 | 10 | |
Solid ceramic | Soft flexible film folies (EBA) | 0.40 | 10 | |
Zero friction | Thin stretched film | 0.20 | 200 | |
Ceramic | White plastic film with additives | 0.38 | 100 | |
Zero friction | Thin stretched film | 0.38 | 100 | |
Titanium | Plastic film with additives | 0.38 | 100 | |
Solid ceramic | Plastic film with additives, multilayer | 0.38 | 30 |
While slitting razor blades are commonly used, other types of slitting knives, such as shear blades, crush cut blades, and score cut blades, may also be employed depending on specific requirements and material characteristics. The choice of slitting knife depends on factors such as material type, thickness, surface finish, and desired slit quality.
Choice of the Right Slitter Knife and Configurations
 The choice of knife configuration, such as shear, razor, crush cut, or score cut, depends on the material being processed and the desired slit quality. Factors such as blade sharpness, angle, and positioning influence the cutting performance and the quality of the finished rolls. Precise adjustment of blade gap, overlap, ensure optimal cutting performance and minimizes material waste. While specific values for factors such as knife positioning, tension control, and slitting speed can vary depending on the material being processed, the equipment used, and other factors, we can provide some general guidelines and recommended values.
The choice of knife configuration, such as shear, razor, crush cut, or score cut, depends on the material being processed and the desired slit quality. Factors such as blade sharpness, angle, and positioning influence the cutting performance and the quality of the finished rolls. Precise adjustment of blade gap, overlap, ensure optimal cutting performance and minimizes material waste. While specific values for factors such as knife positioning, tension control, and slitting speed can vary depending on the material being processed, the equipment used, and other factors, we can provide some general guidelines and recommended values.
Tips from Sollex on how to choose and maintain slitter blades
- Blade angle depends on the material being cut and the desired edge quality. Optimal choice of cutting angle for razor slitting is 45 degrees, shear cutting - 90 degrees.
- Blades must always be sharp to maintain optimum cutting performance. Keep a full stock of new replacement blades for continuous production.
- Match the blades to the thickness of the material to be cut. Depending on the type of material being cut on the slitter, additives, and cutting speed, the thickness of the blades plays a major role.
- Material elasticity influences tension control requirements. Higher elasticity may require more precise tension control to prevent stretching or wrinkling.
- Surface treatments, coatings, or finishes may affect cutting performance.
- Ideally, tension variation should be kept within ±5% of the target tension to ensure consistent slitting and rewinding.
- Match the blades to the thickness of the material to be cut. Depending on the type of material being cut on the slitter, the additives in the film, and the cutting speed, the thickness and coating of the blades plays a major role. If the film cutting speed is too fast, the blade edges will heat up and the film will melt, significantly reducing the quality of the product. Blade coating can reduce edge heating from friction.
- In shear slitting there are 4 important factors influencing the quality cut, which are blades overlap (0.50 to 0.75 mm) ,cut point, side loading pressure, cant angle (0.25 degrees for films), slitter and web speed, blade profiles.
But remember! These are general guidelines and specific values may need to be adjusted depending on factors such as material characteristics, machine capabilities and production requirements. Tests and experiments should be conducted to determine the optimum settings for your specific application. In addition, consulting with equipment manufacturers or industry experts can provide valuable ideas and recommendations for achieving the best results in slitting and rewinding operations.





